Filtering Functionality
The project focused on redesigning the filtering functionality by consolidating multiple components and steps into a single space, improving discoverability, usability, and reducing the learning curve.
Research & analysis / UX / UI
2024
Encare is a HealthTech company based in Stockholm, specializing in the development of cloud-based solutions to enhance surgical care.
EIAS, ERAS® Interactive Audit System, is a comprehensive software solution developed by Encare to support the implementation of ERAS protocols in hospitals. It offers functionalities such as data entry, analysis, and reporting.
Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) protocols aim to improve patient outcomes by reducing complications and shortening hospital stays.
EIAS, ERAS® Interactive Audit System, is a comprehensive software solution developed by Encare to support the implementation of ERAS protocols in hospitals. It offers functionalities such as data entry, analysis, and reporting.
Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) protocols aim to improve patient outcomes by reducing complications and shortening hospital stays.
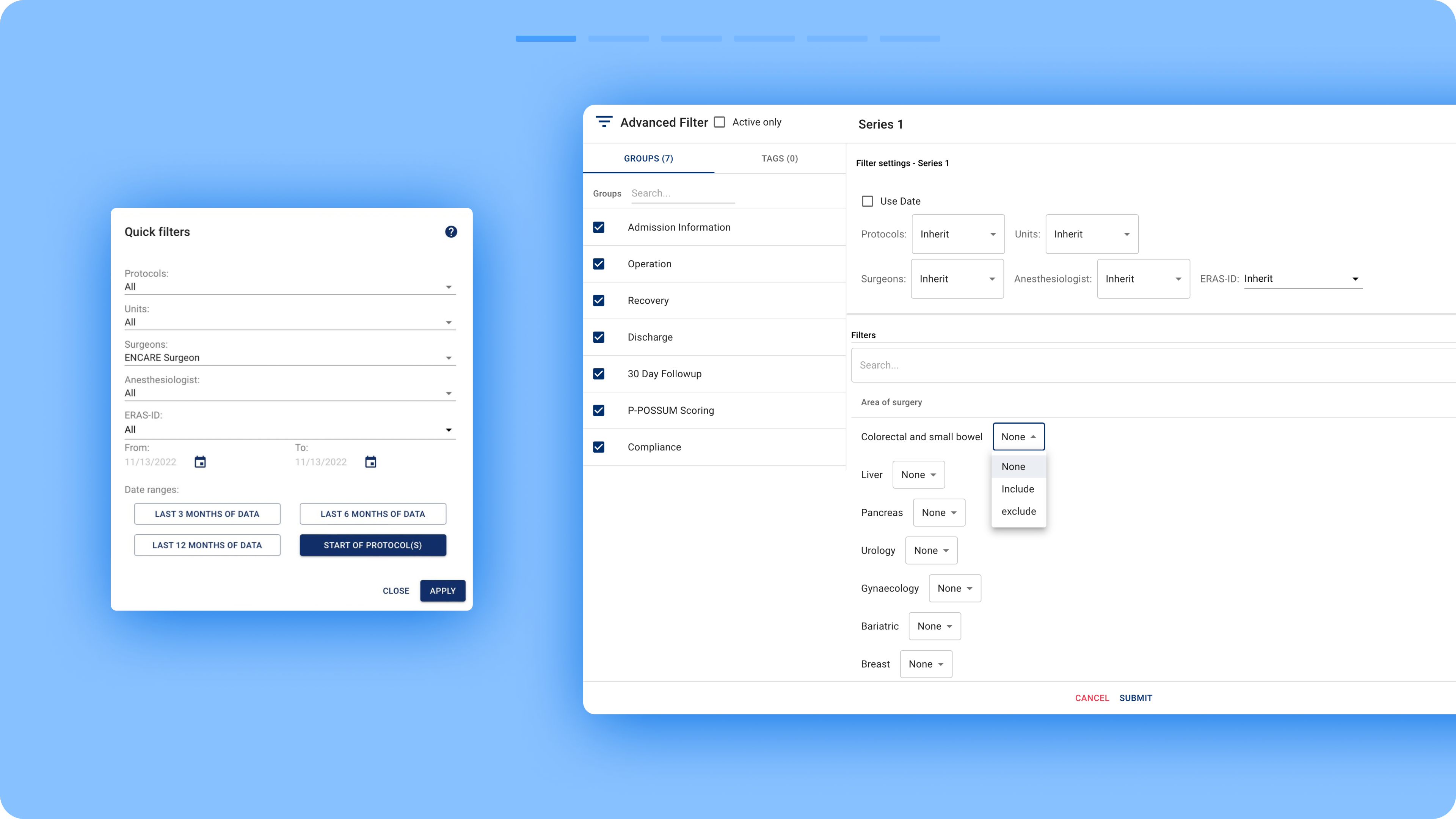
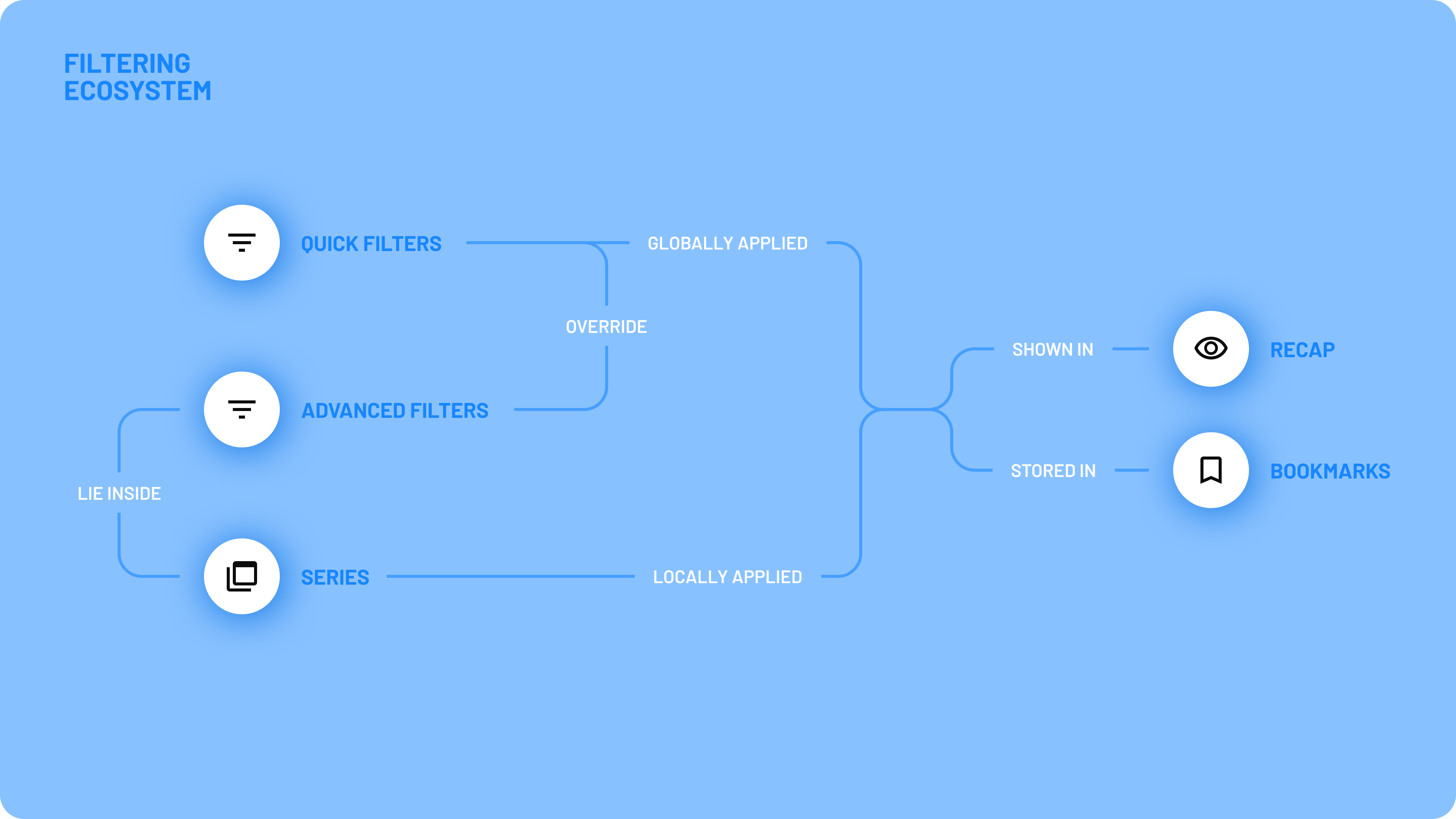
Previous filtering ecosystem
The problem :
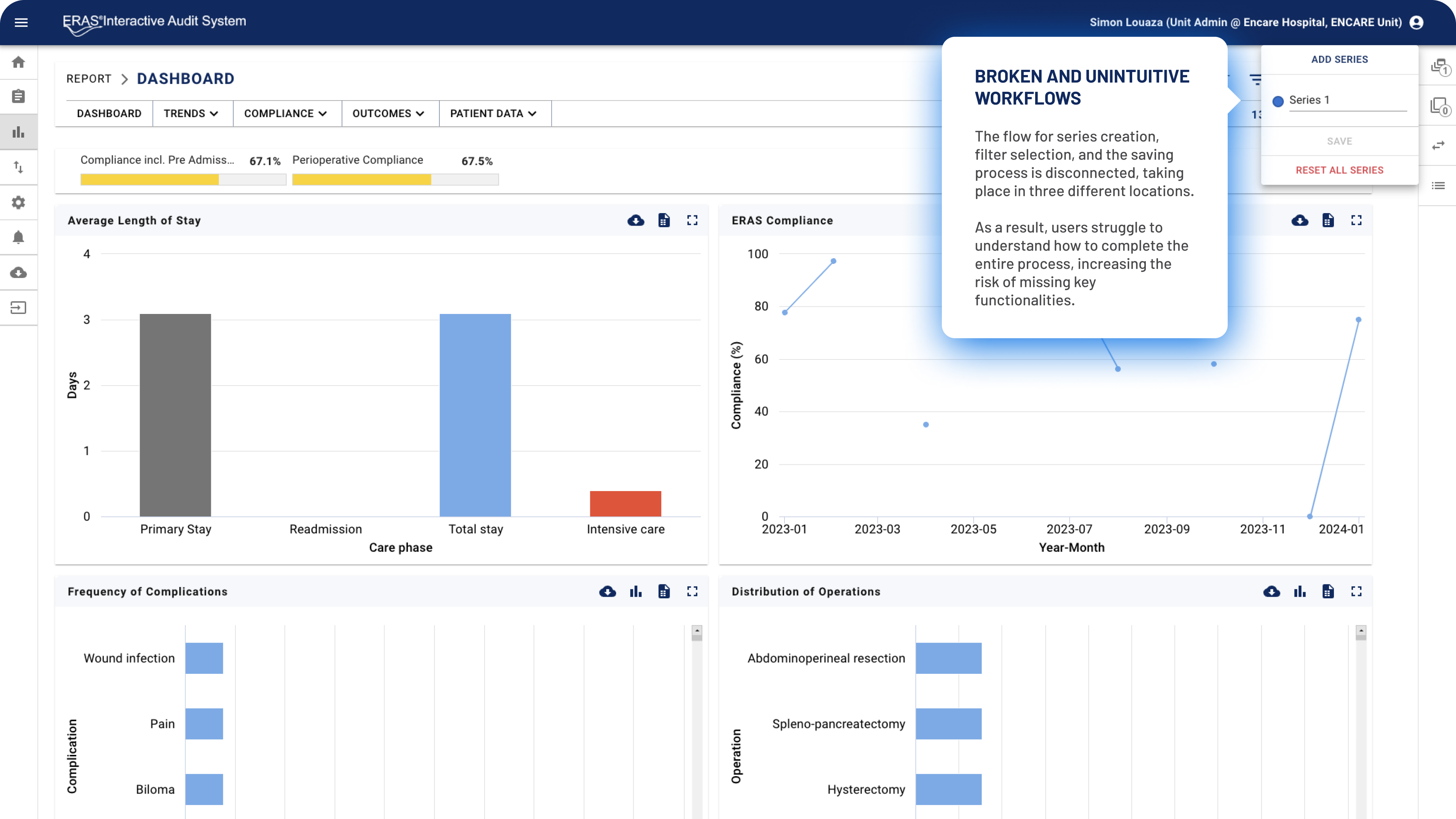
The previous filtering ecosystem consisted of multiple components that were part of a shared flow but scattered across different areas of the interface. This made it extremely difficult for users to locate all elements, understand their connections, and effectively use the filtering functionality.
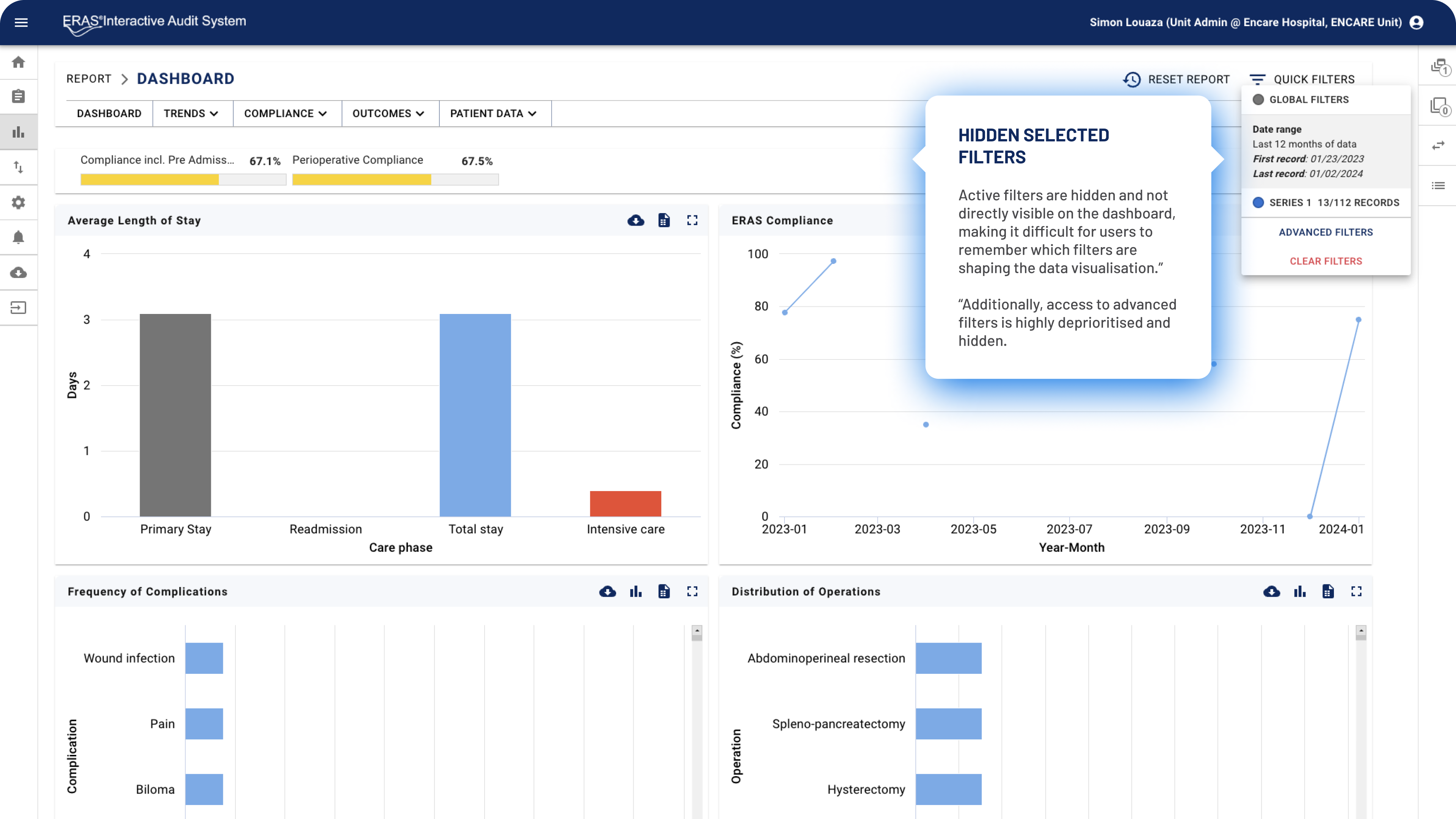
Several components were tucked away in secondary spaces with unclear activation affordances. Additionally, the filter recap made it difficult for users to understand what filters were shaping the dashboard data. Instead, filter chips should have been displayed directly within the interface.
The filtering mechanism also suffered from unintuitive logic. Quick filter selections would override selections for the same parameters inside each series, often without users realizing it.
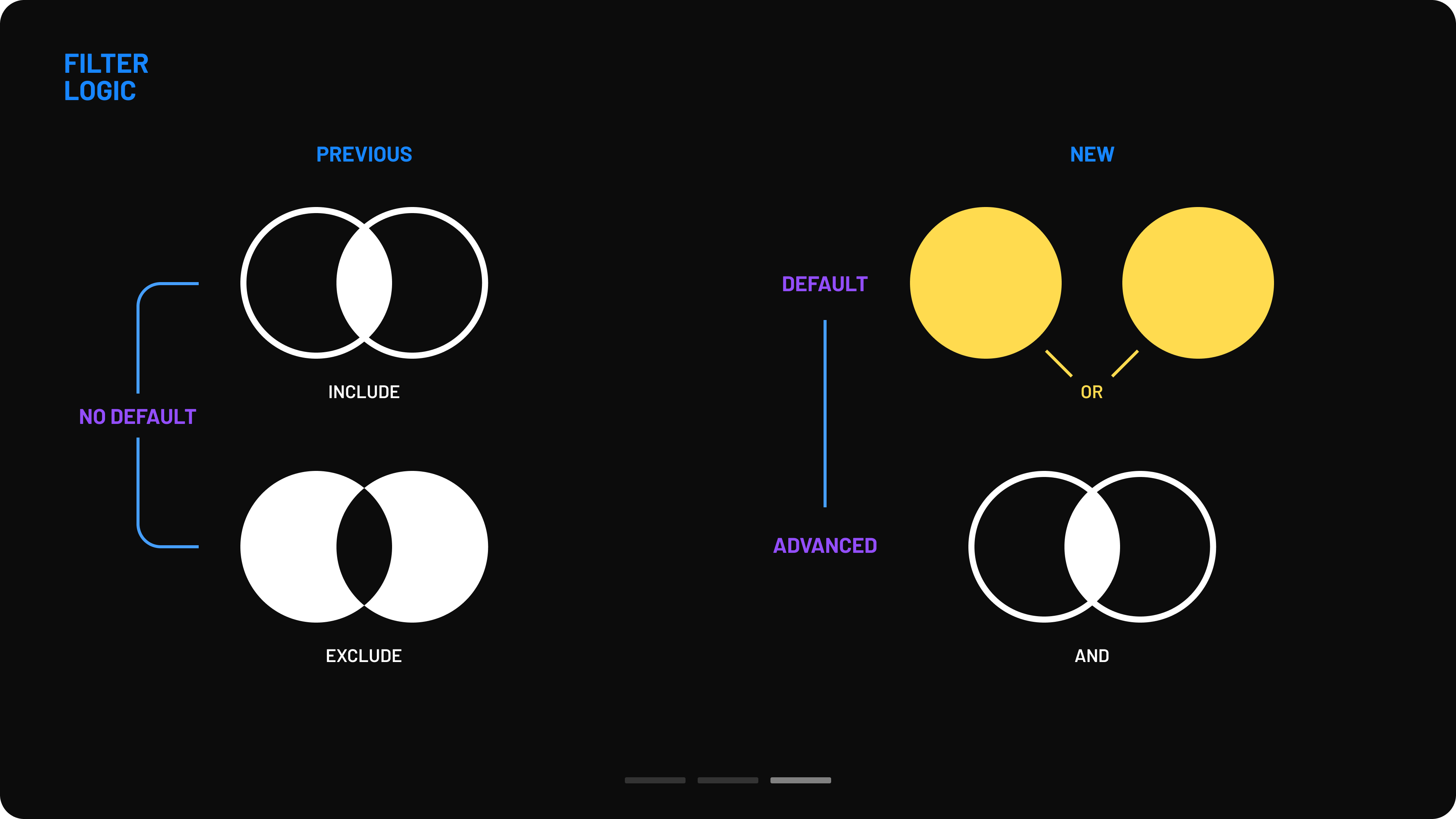
Moreover, filters applied an AND logic by default, frequently resulting in no valid data (e.g. selecting both “female” and “male” would yield no results, as no patient can be both). A more intuitive OR logic, which better aligns with users’ mental models, would have improved usability.
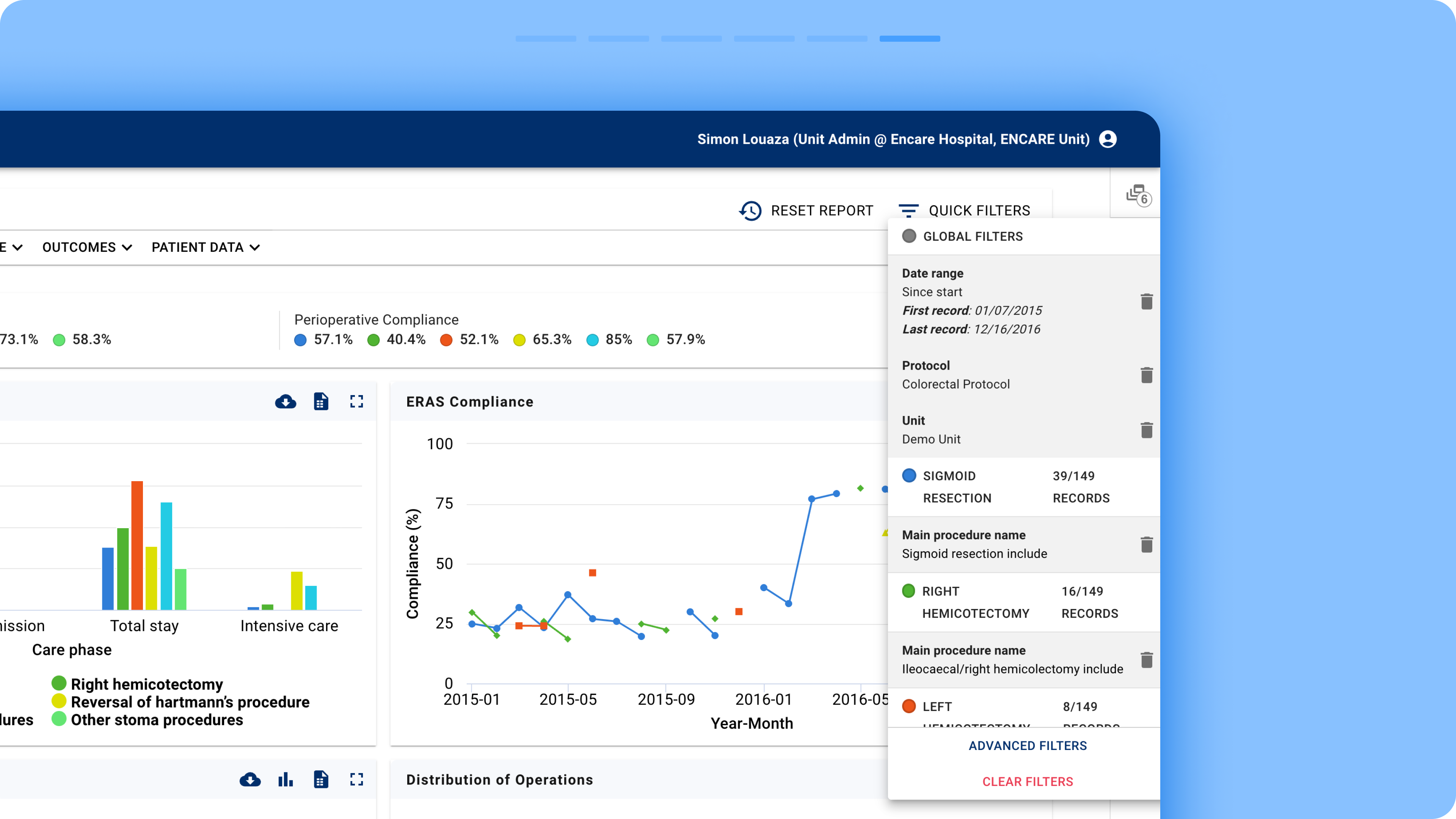
- Quick Filters: Misleadingly named, as they were simply ordinary filters placed in a modal. They were intended to highlight the most commonly used filters.
-
Advanced Filters: A comprehensive list of filters categorized by the different phases of the surgical cycle, from admission to discharge and follow-up.
-
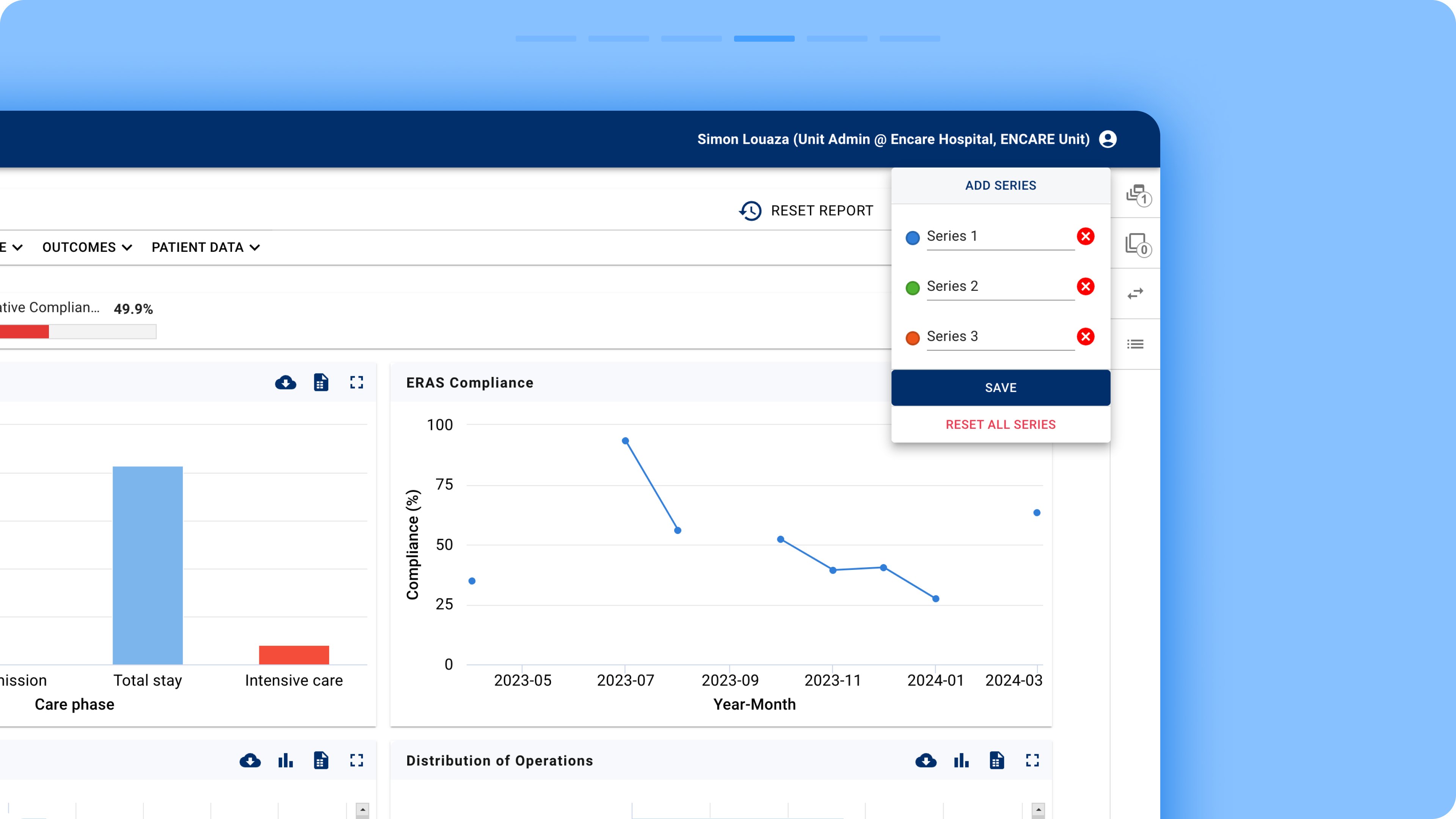
Series: A feature that allows users to create control groups and compare different sets of filters. Users can create up to eight series.
-
Filter Recap: A hidden popup, accessible via an item in the right bar menu, summarizing active filters.
-
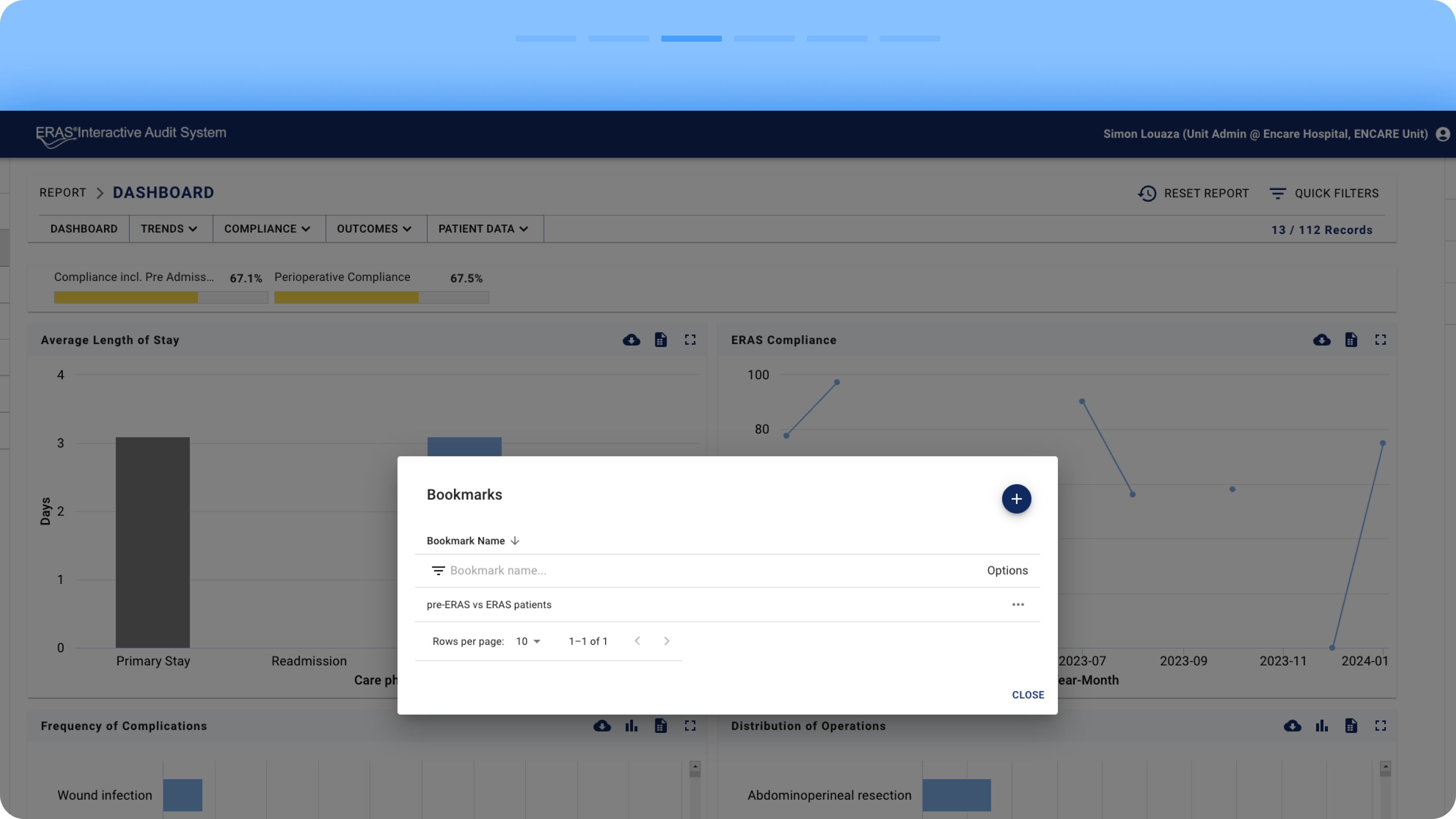
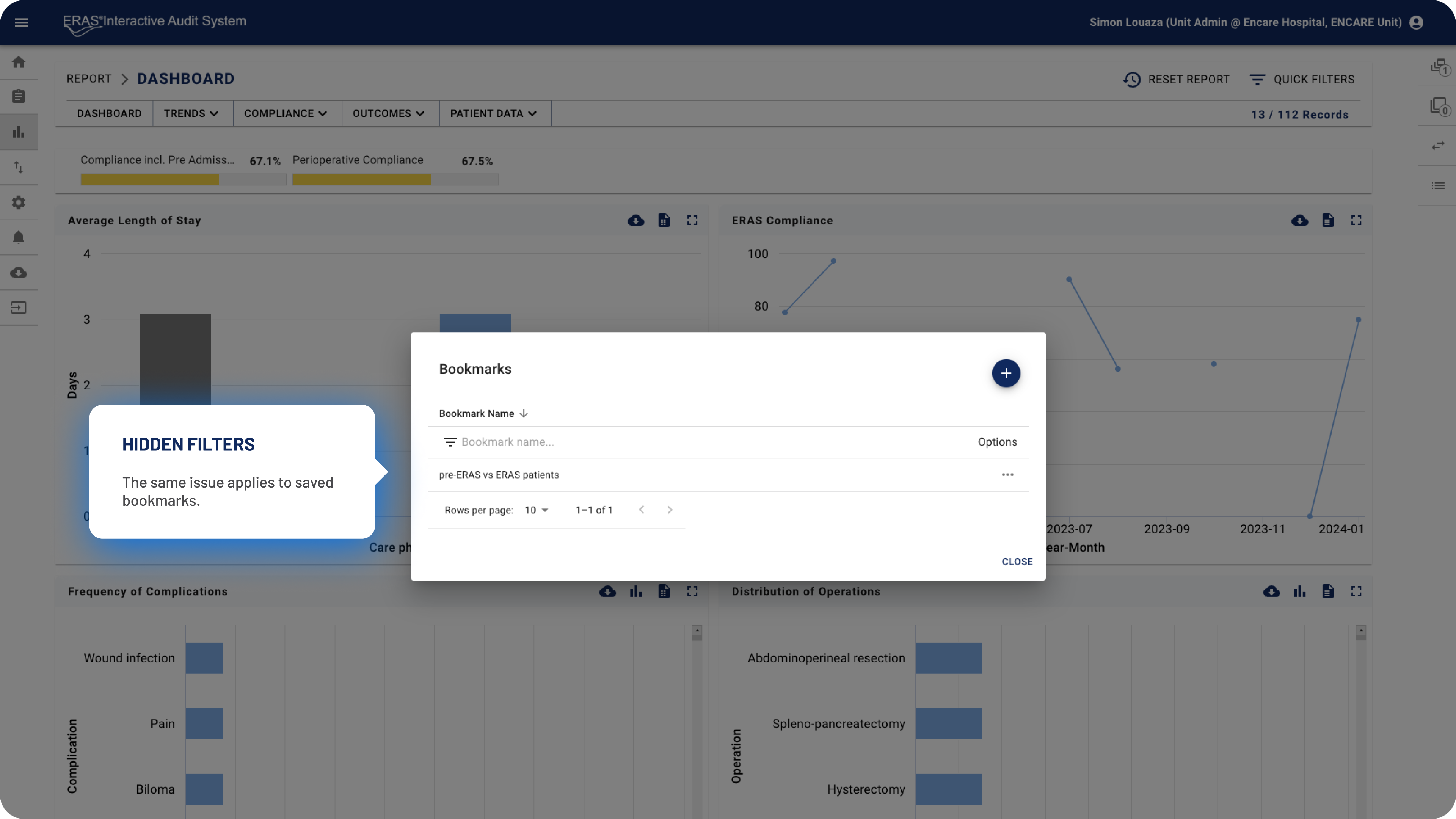
Bookmarks: A space for saving sets of active filters.
Several components were tucked away in secondary spaces with unclear activation affordances. Additionally, the filter recap made it difficult for users to understand what filters were shaping the dashboard data. Instead, filter chips should have been displayed directly within the interface.
The filtering mechanism also suffered from unintuitive logic. Quick filter selections would override selections for the same parameters inside each series, often without users realizing it.
Moreover, filters applied an AND logic by default, frequently resulting in no valid data (e.g. selecting both “female” and “male” would yield no results, as no patient can be both). A more intuitive OR logic, which better aligns with users’ mental models, would have improved usability.
Browse the gallery to explore the research findings


The solution :
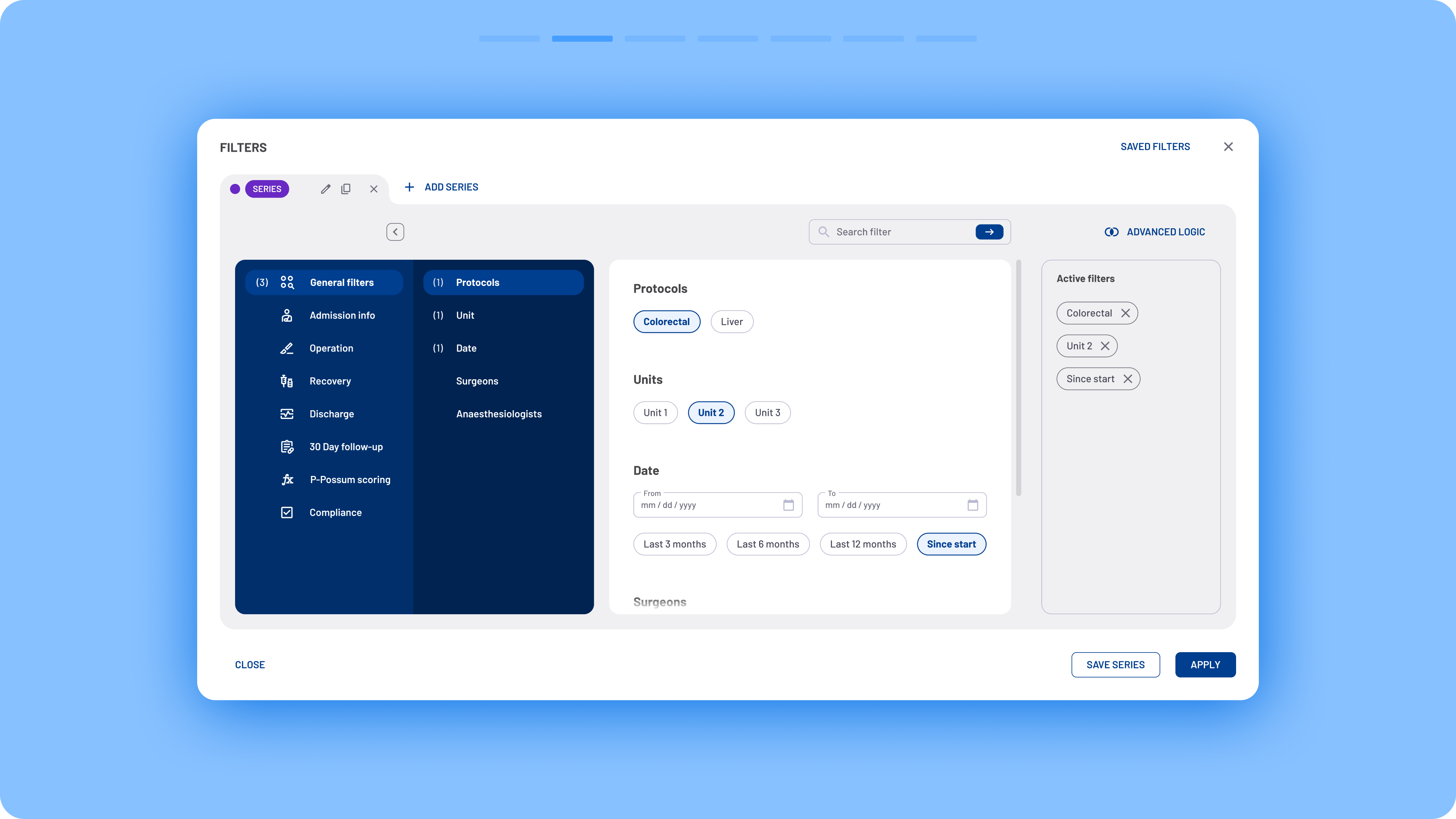
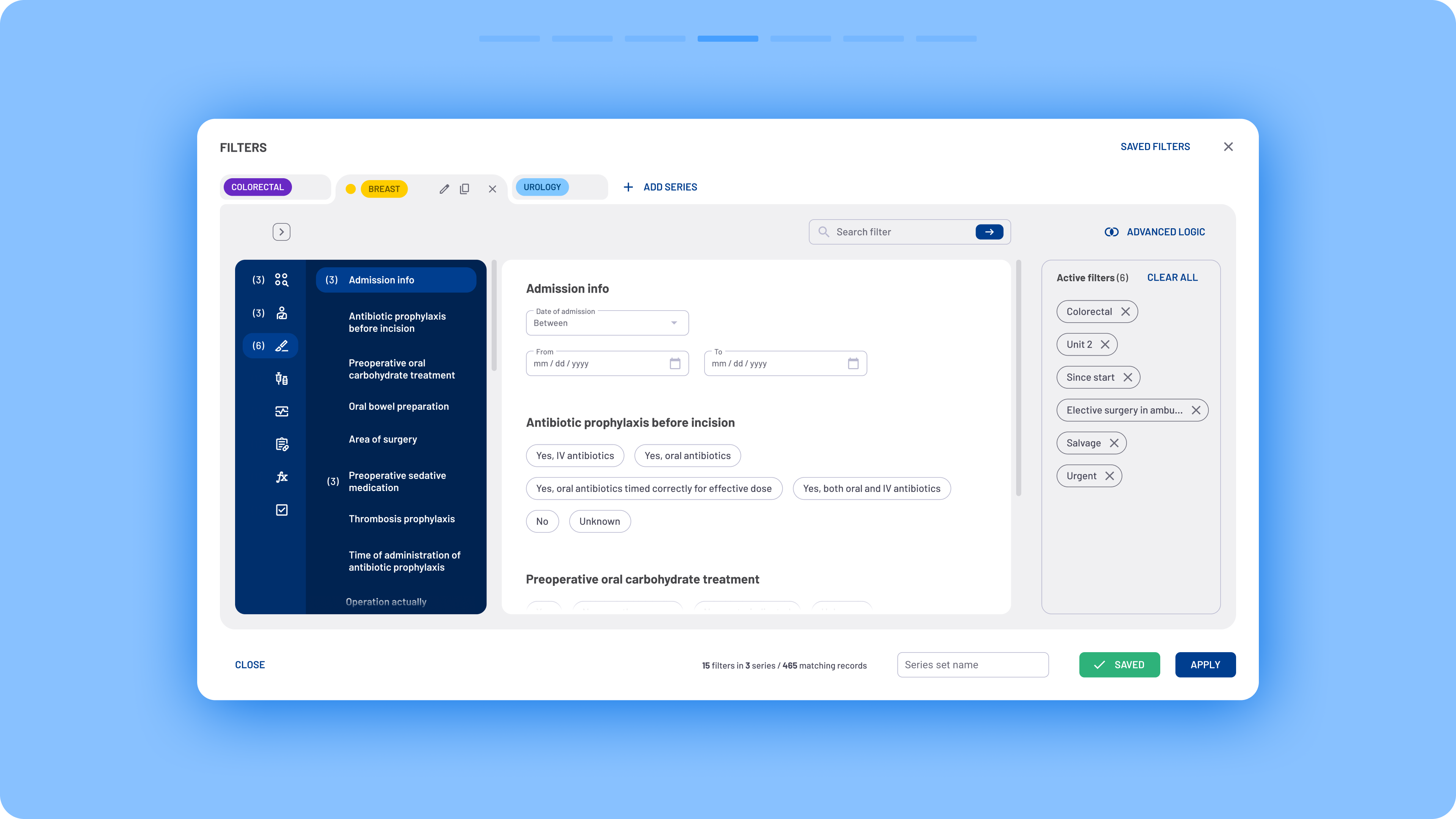
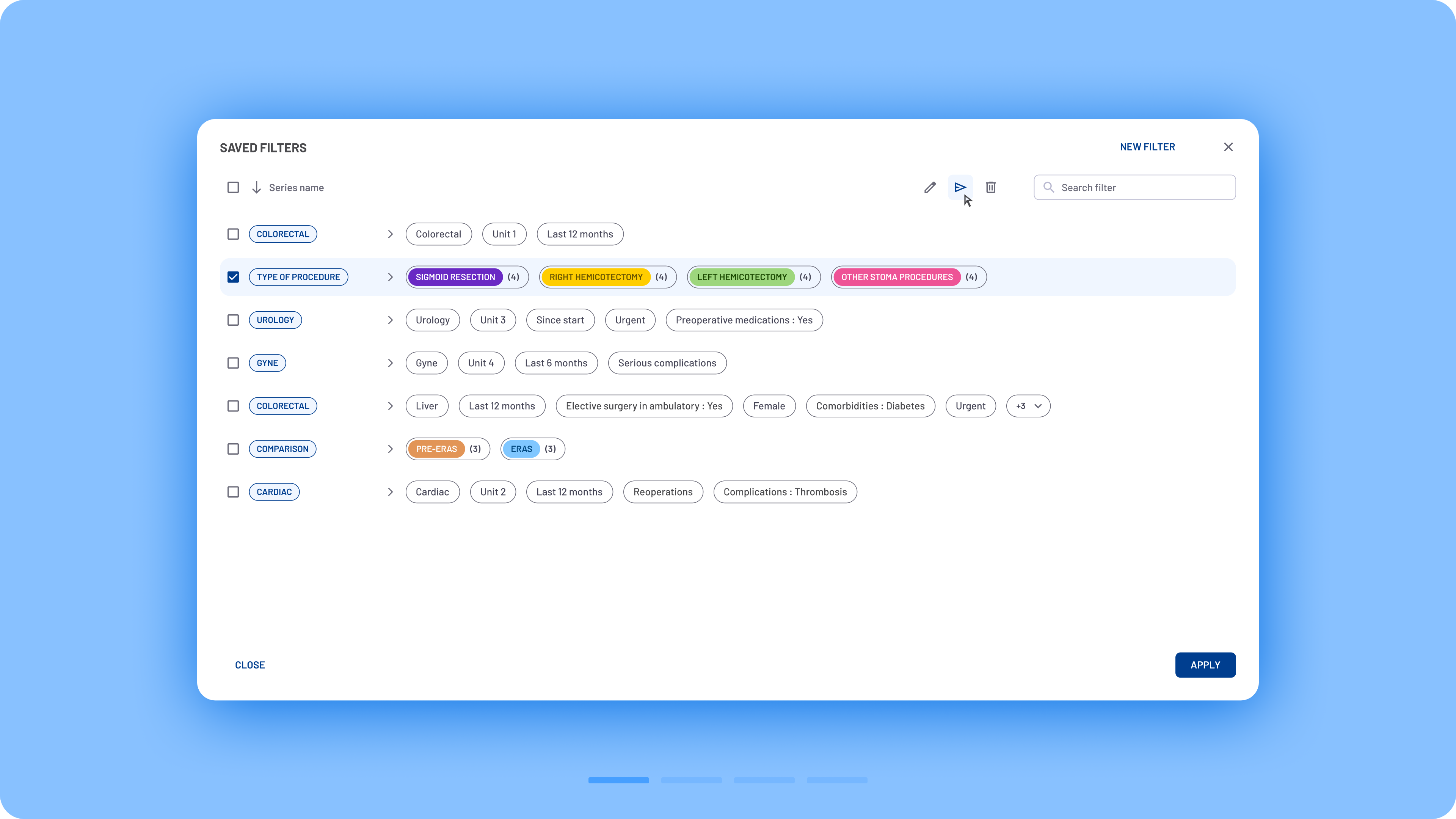
In the new design, quick filters, advanced filters, and series creation were merged into a single modal box that functions similarly to a web browser. Users can create multiple series, similar to browser tabs, and assign a unique set of filters to each one.
Browse the gallery to view the redesigned flow
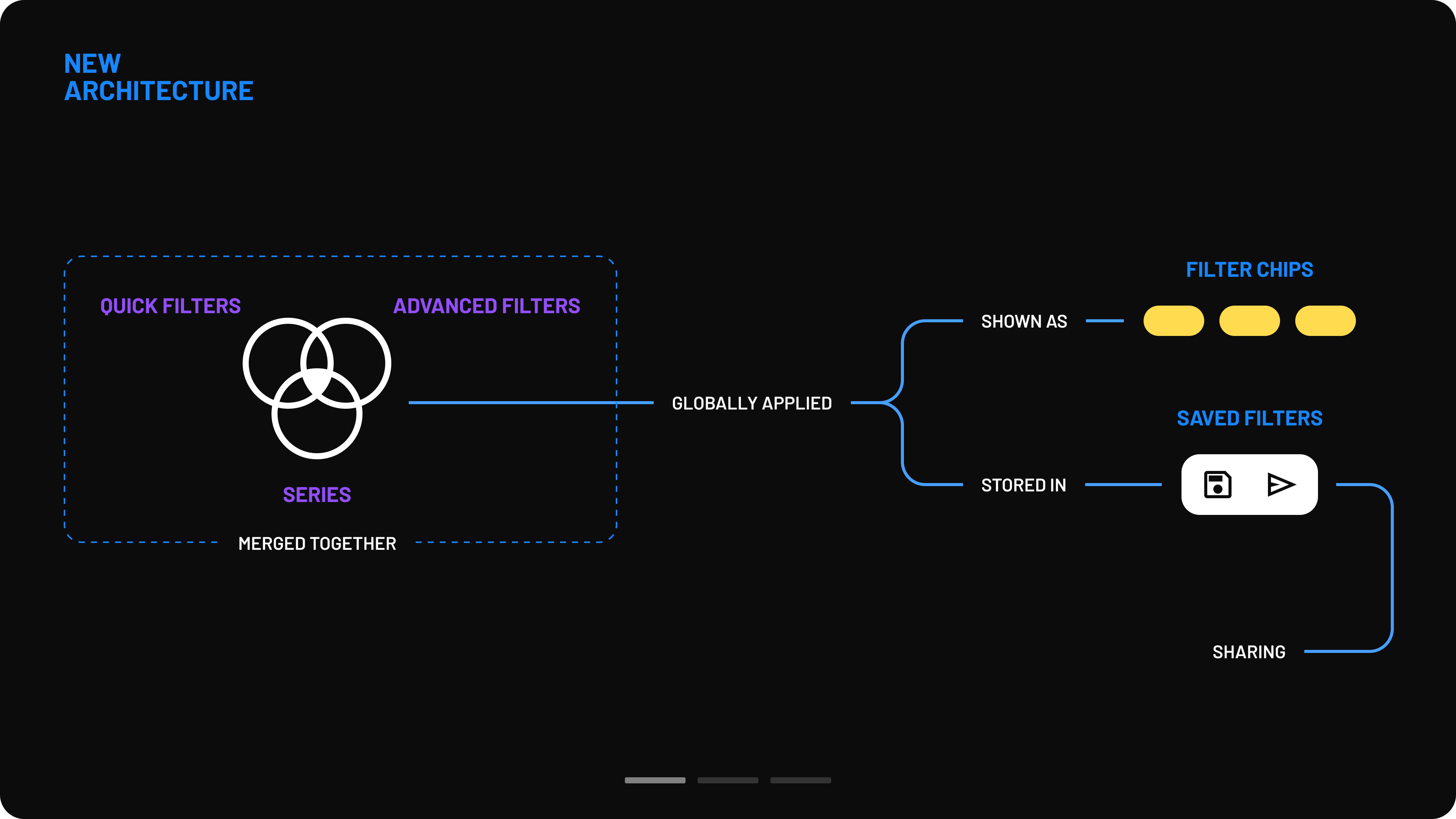
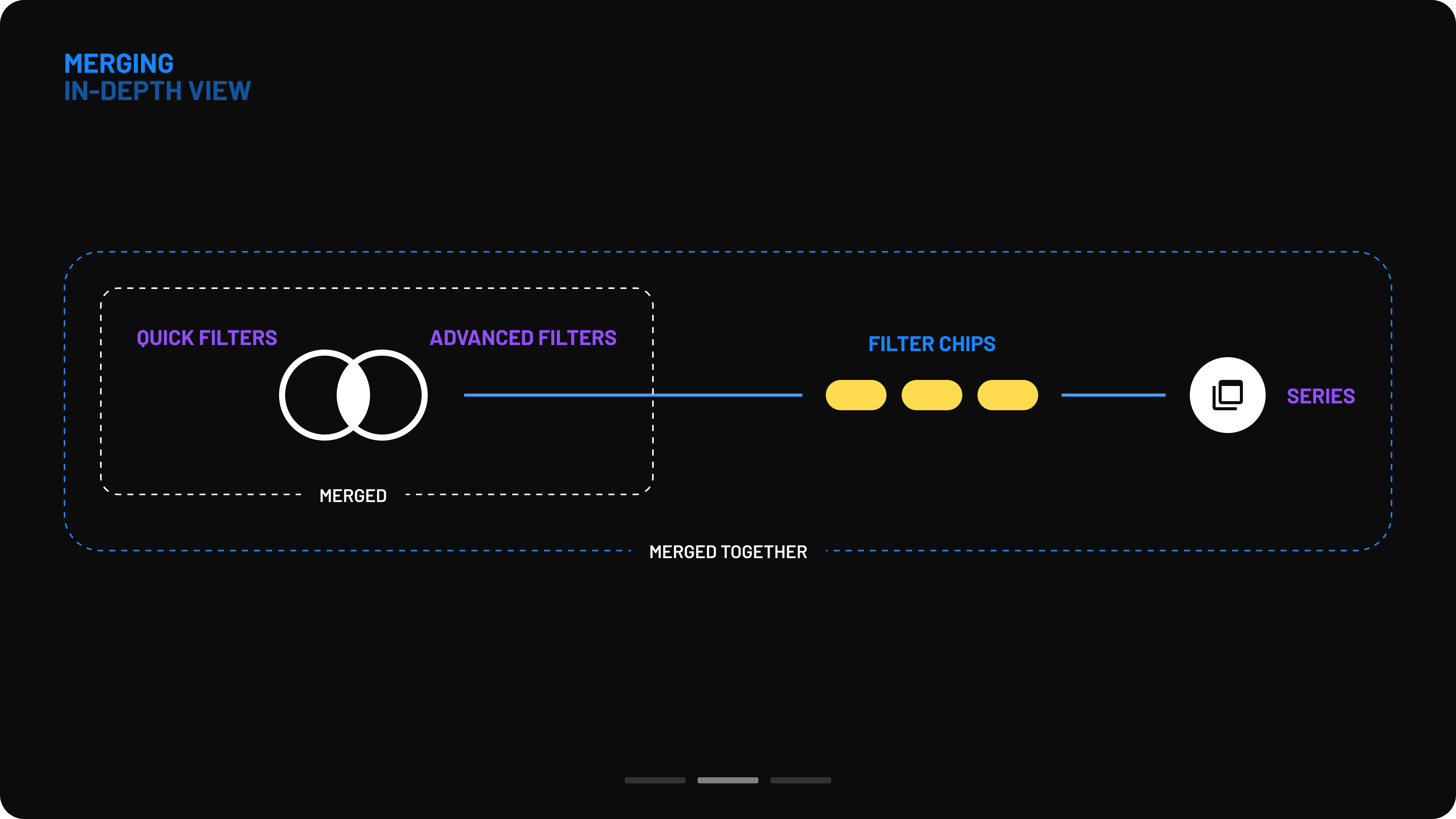
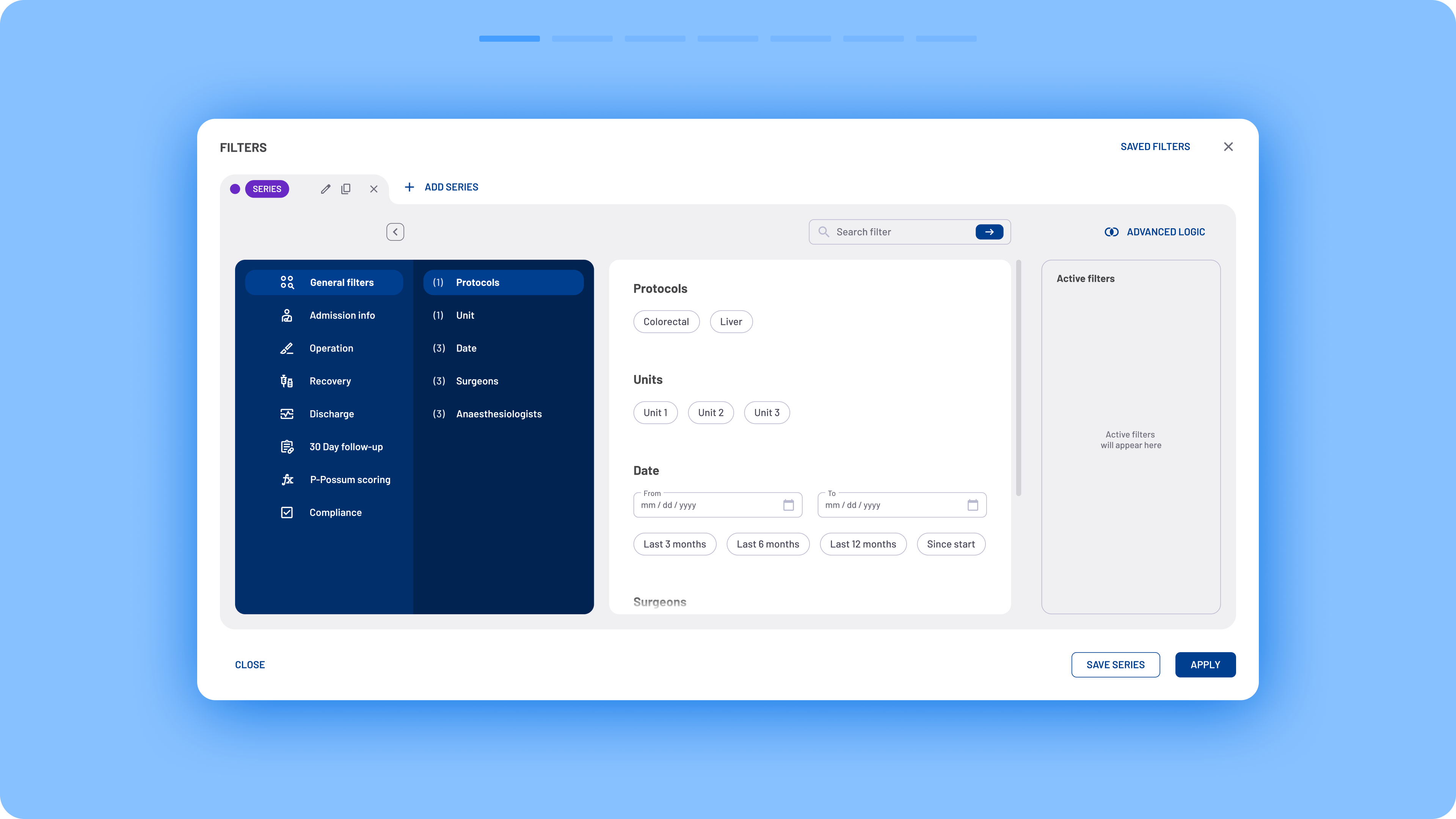
Navigation was completely redesigned to improve usability. Previously, users had to select checkboxes from multiple filter sections, resulting in an overwhelming list of matching filters. Now, a two-column menu layout provides a clearer overview with minimal scrolling. Filters are categorized according to the different stages of the surgical process.
Several key usability improvements were introduced:
Several key usability improvements were introduced:
- Simplified filter selection: Instead of using dropdowns to define filter logic (include/exclude), users can now activate filters directly via clickable filter chips.
-
Clear filter recap: A summary of active filters is always visible on the right side of the modal box.
-
Streamlined saving process: Users can now save filter sets instantly, without first applying them or opening an additional modal to name them.
-
Persistent filter visibility: Filter chips are now displayed directly on the interface, making it easier to understand which filters are shaping the data.
Explore the new filtering functionality


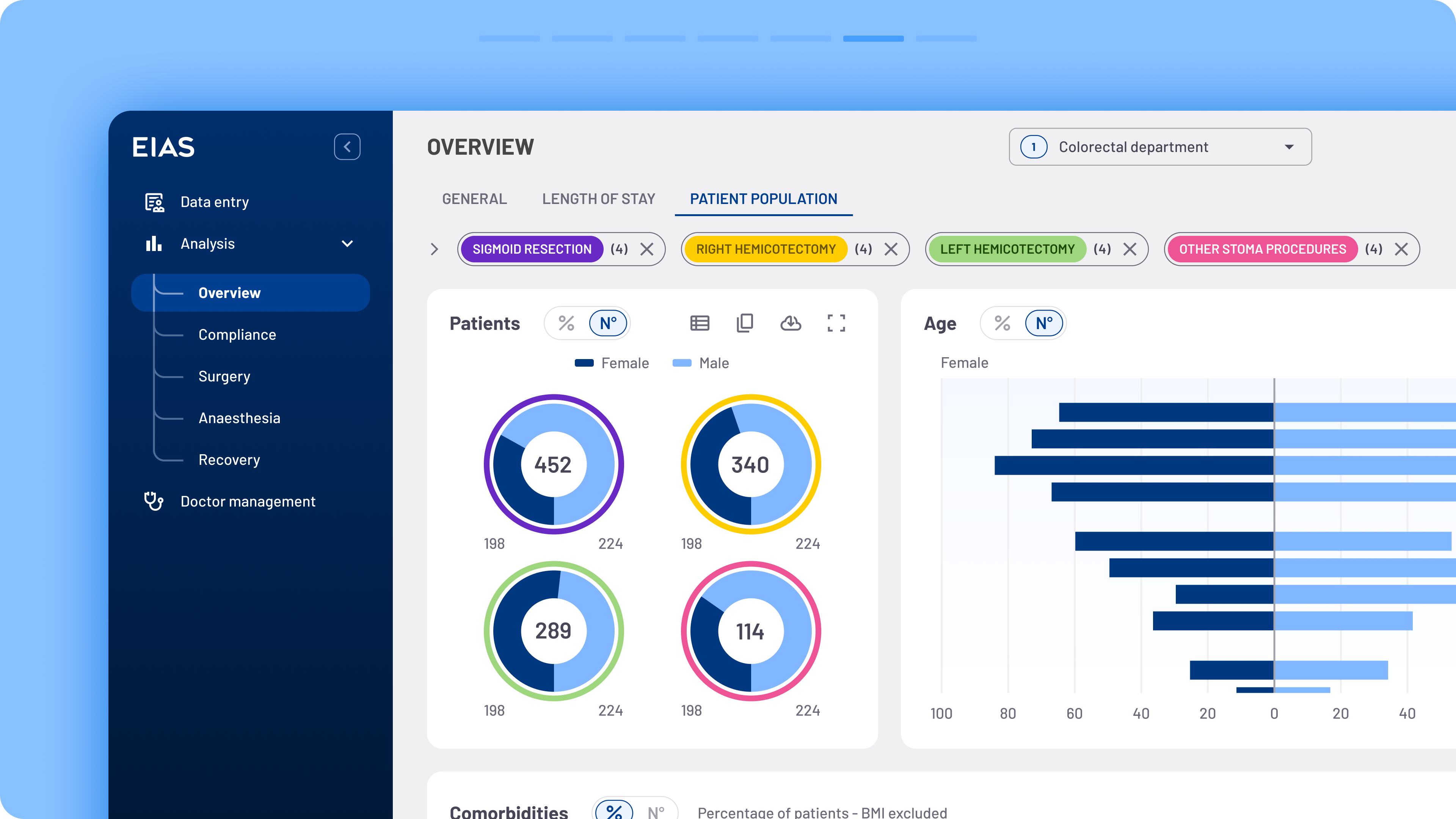
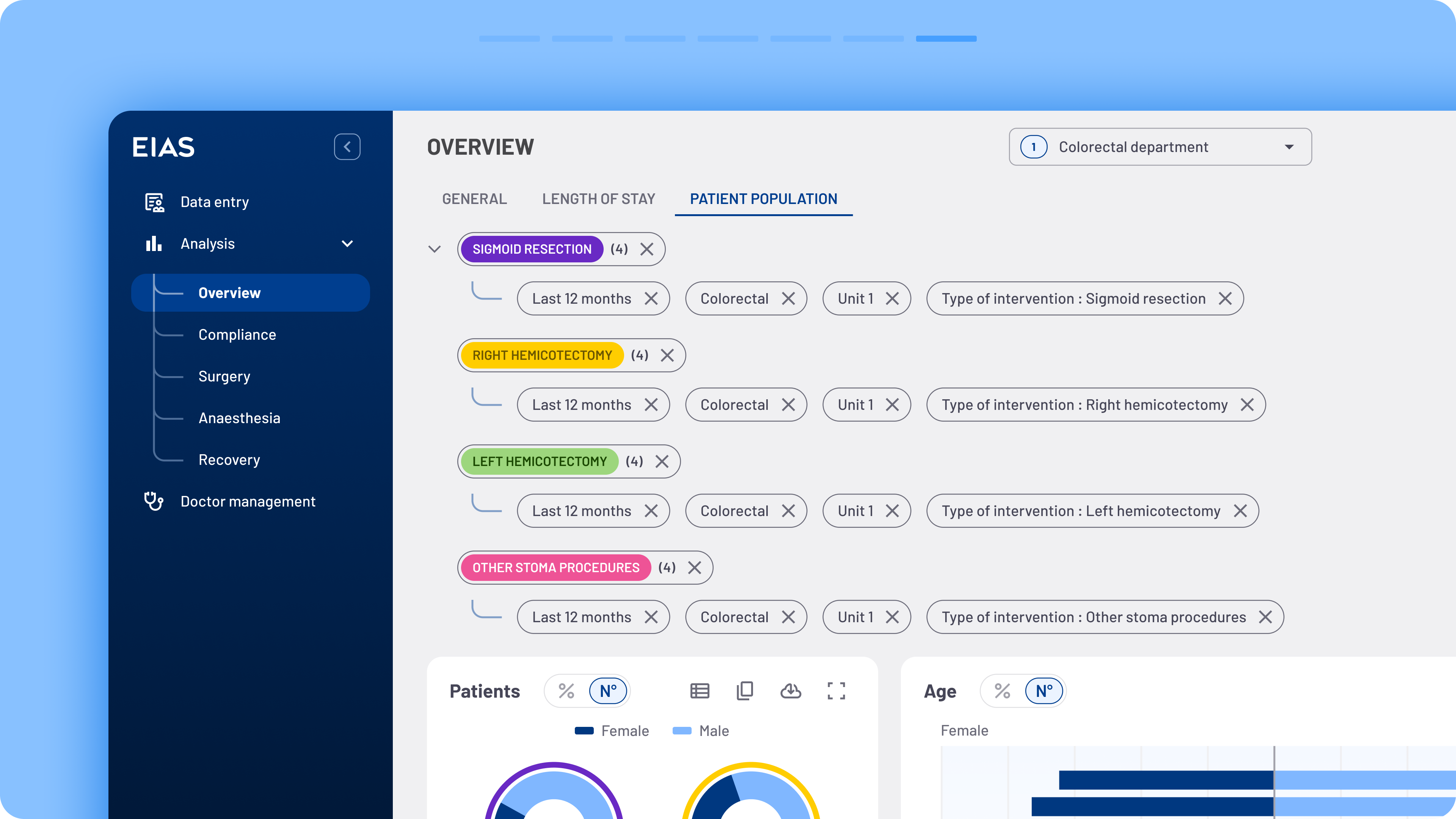
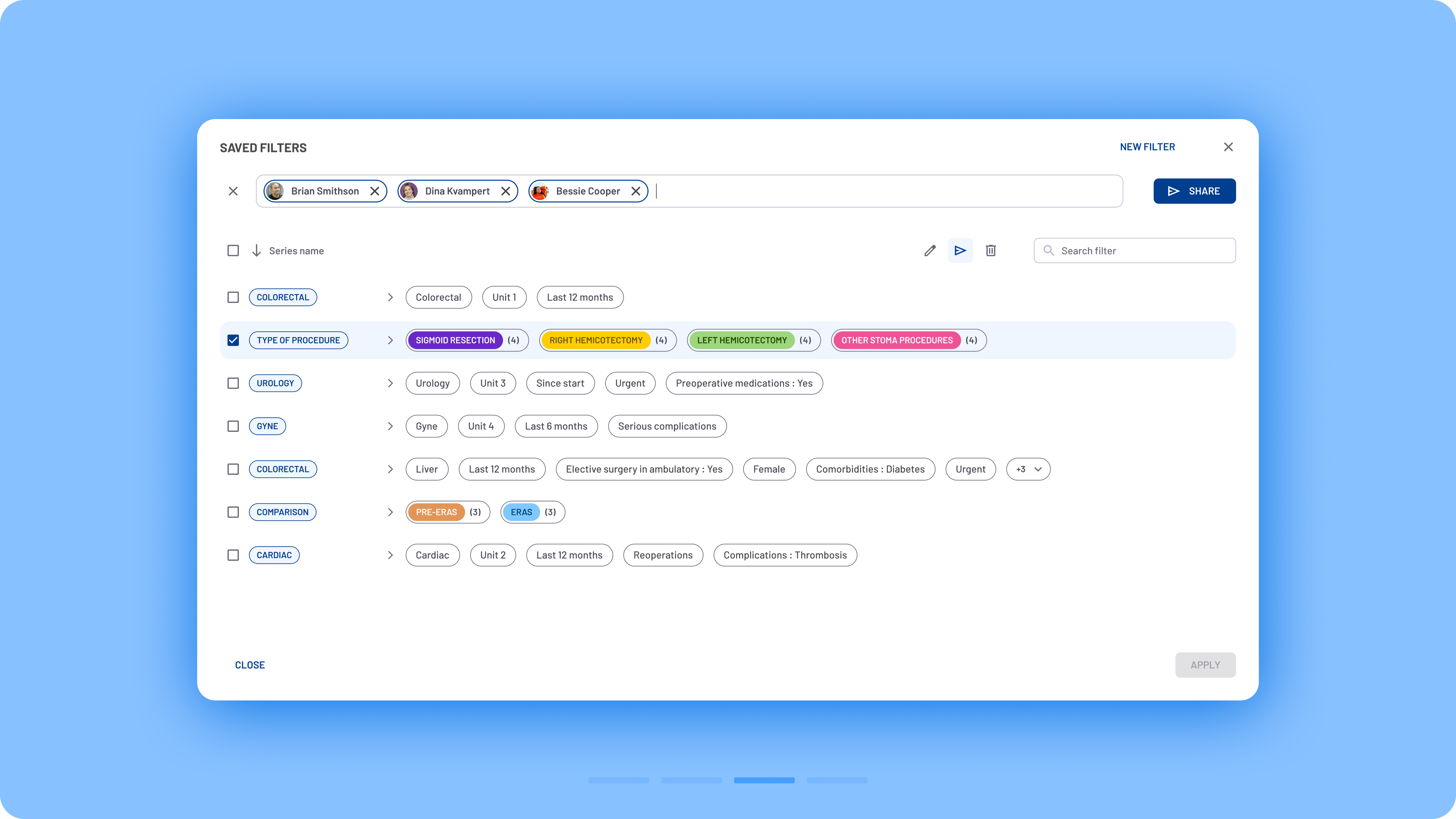
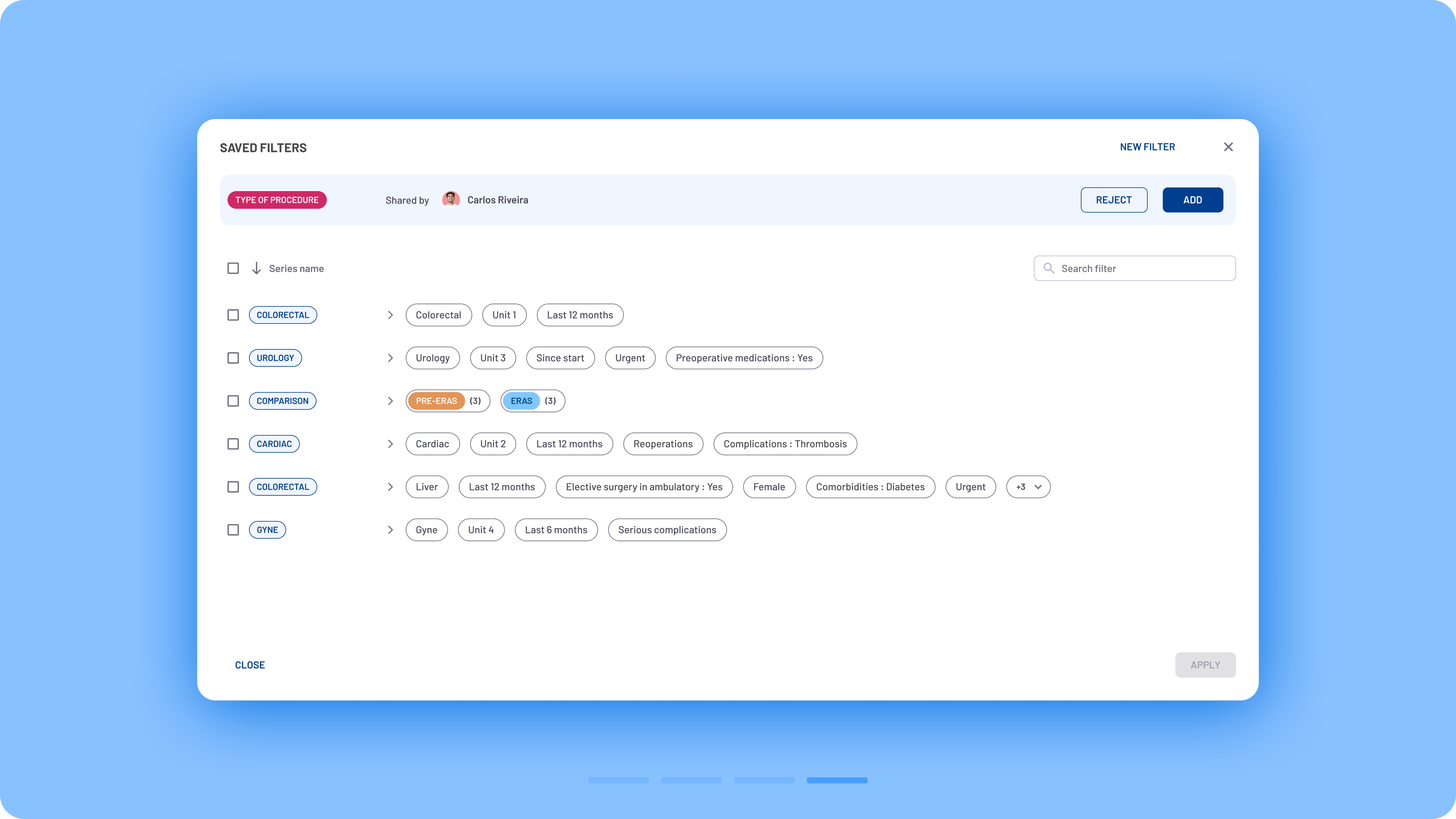
Users frequently requested the ability to share filters with colleagues instead of starting the process from scratch each time. To address this, a new sharing functionality was introduced.
The former Bookmarks space was renamed to the more intuitive Saved Filters modal, where users can easily share filters by clicking the Share button. They can enter colleagues’ names to send them the selected filters.
The former Bookmarks space was renamed to the more intuitive Saved Filters modal, where users can easily share filters by clicking the Share button. They can enter colleagues’ names to send them the selected filters.
Filter sharing flow

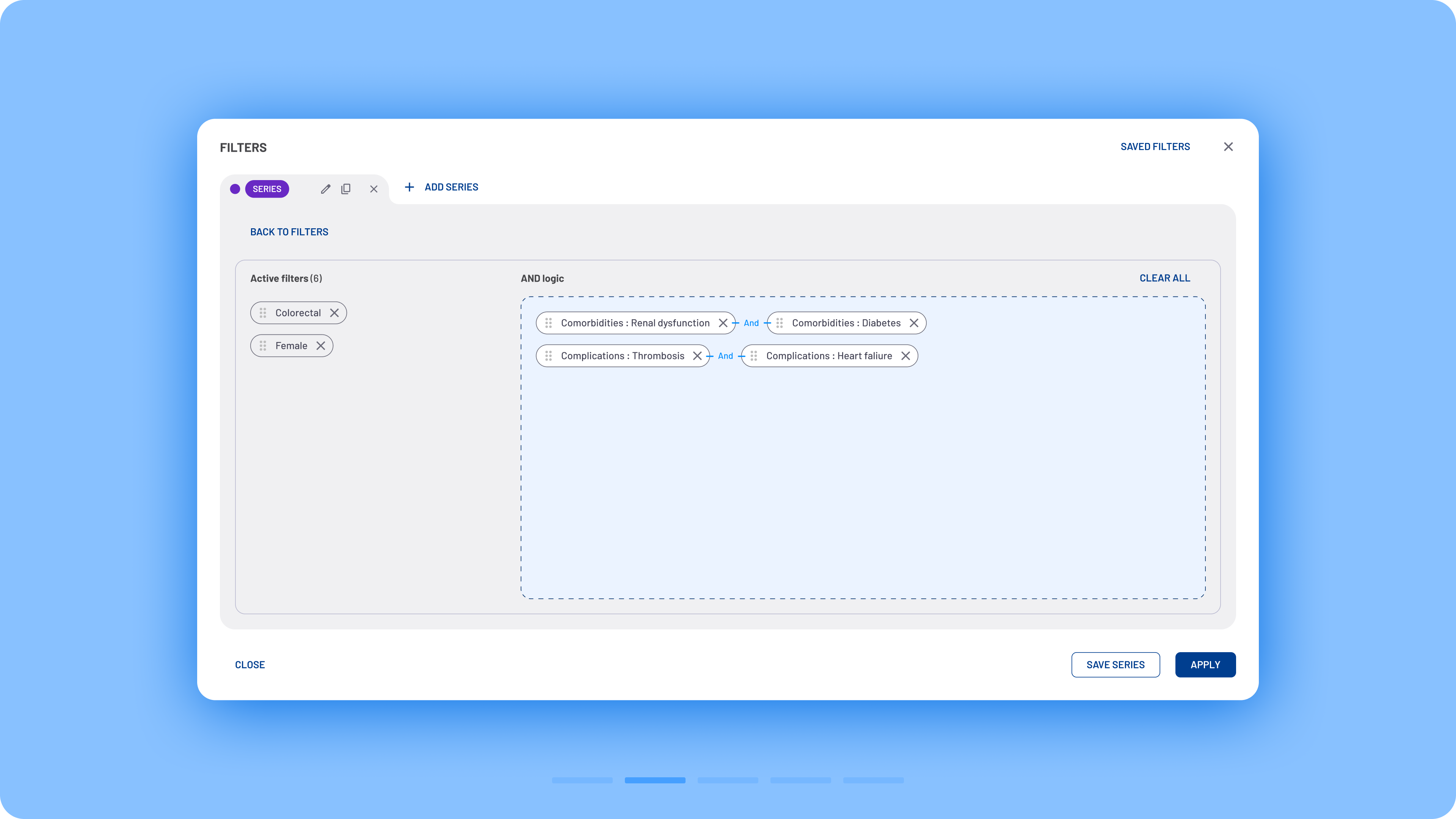
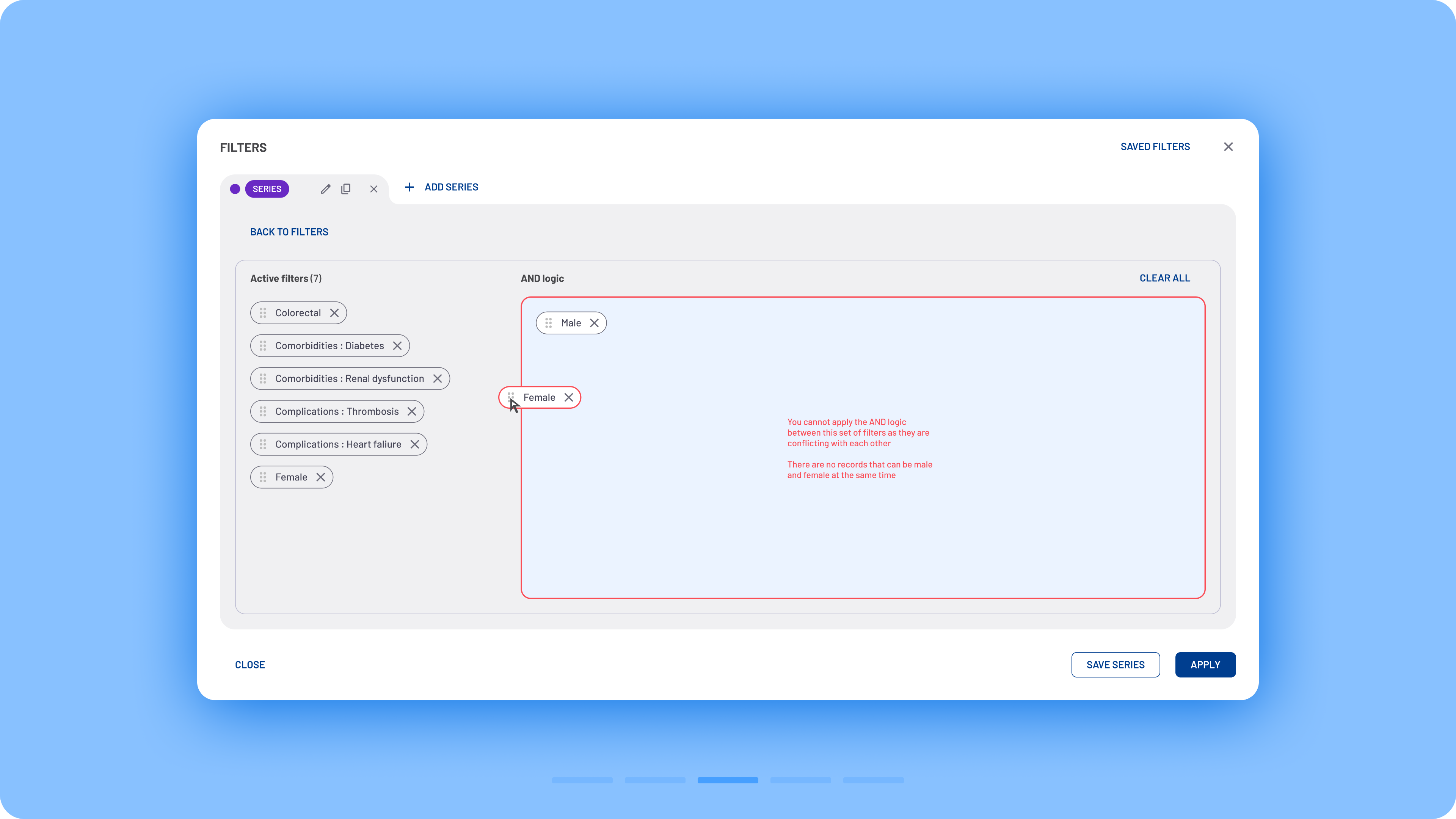
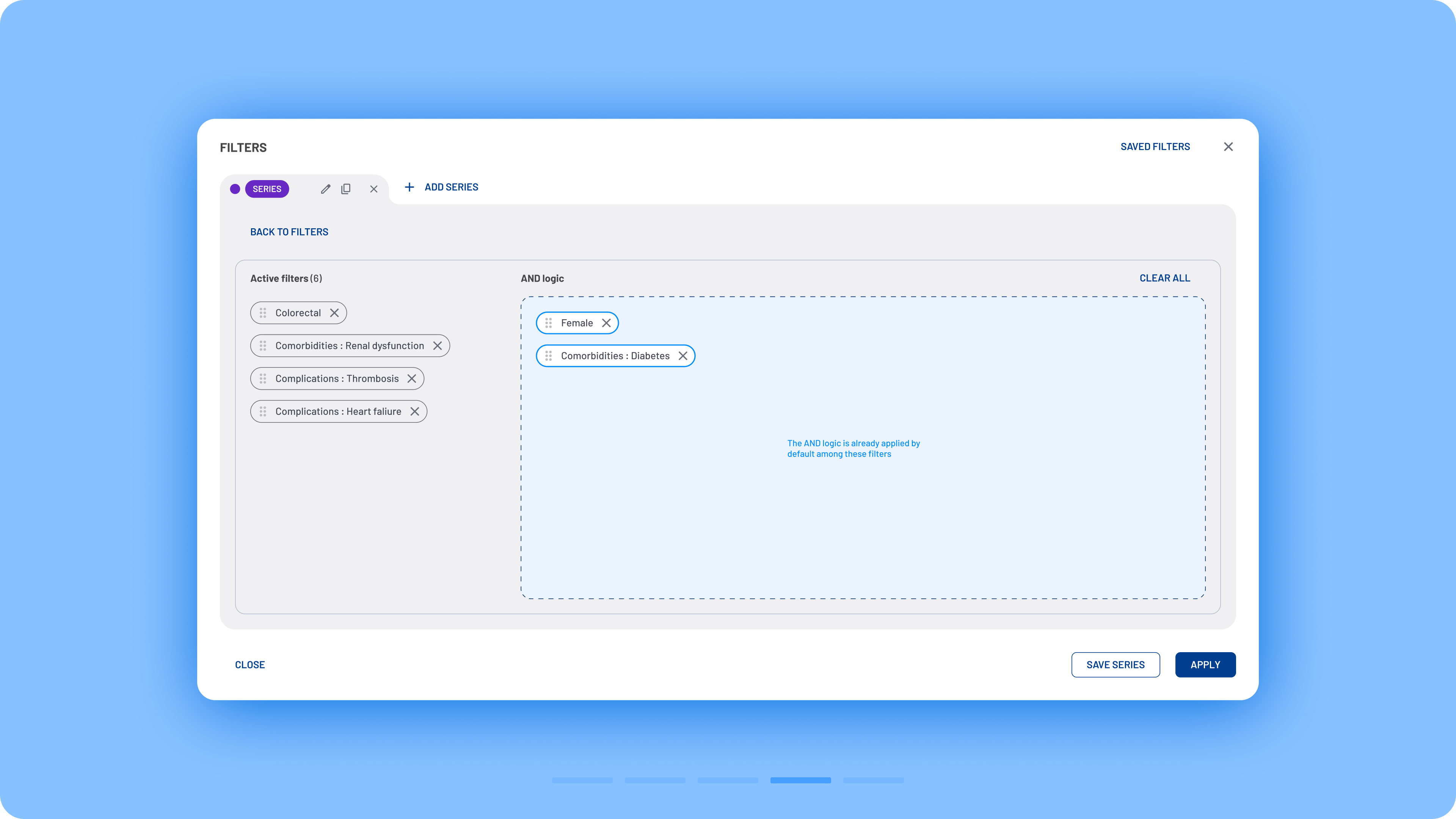
A new option was developed, allowing users to apply AND logic for specific filtering edge cases. This functionality is accessible via the Advanced Logic button in the filter modal. Within the modal, users can also see a recap of active filters along with a drag-and-drop area. Users can drag filters into this area to enforce AND logic and receive guidance on potential incorrect combinations when necessary.
Advanced AND logic flow


Finally, the newly developed EIAS Design System was applied to all new filtering components to enhance the experience, improve
scanability, and allow users to navigate different parts more easily when searching for filters.
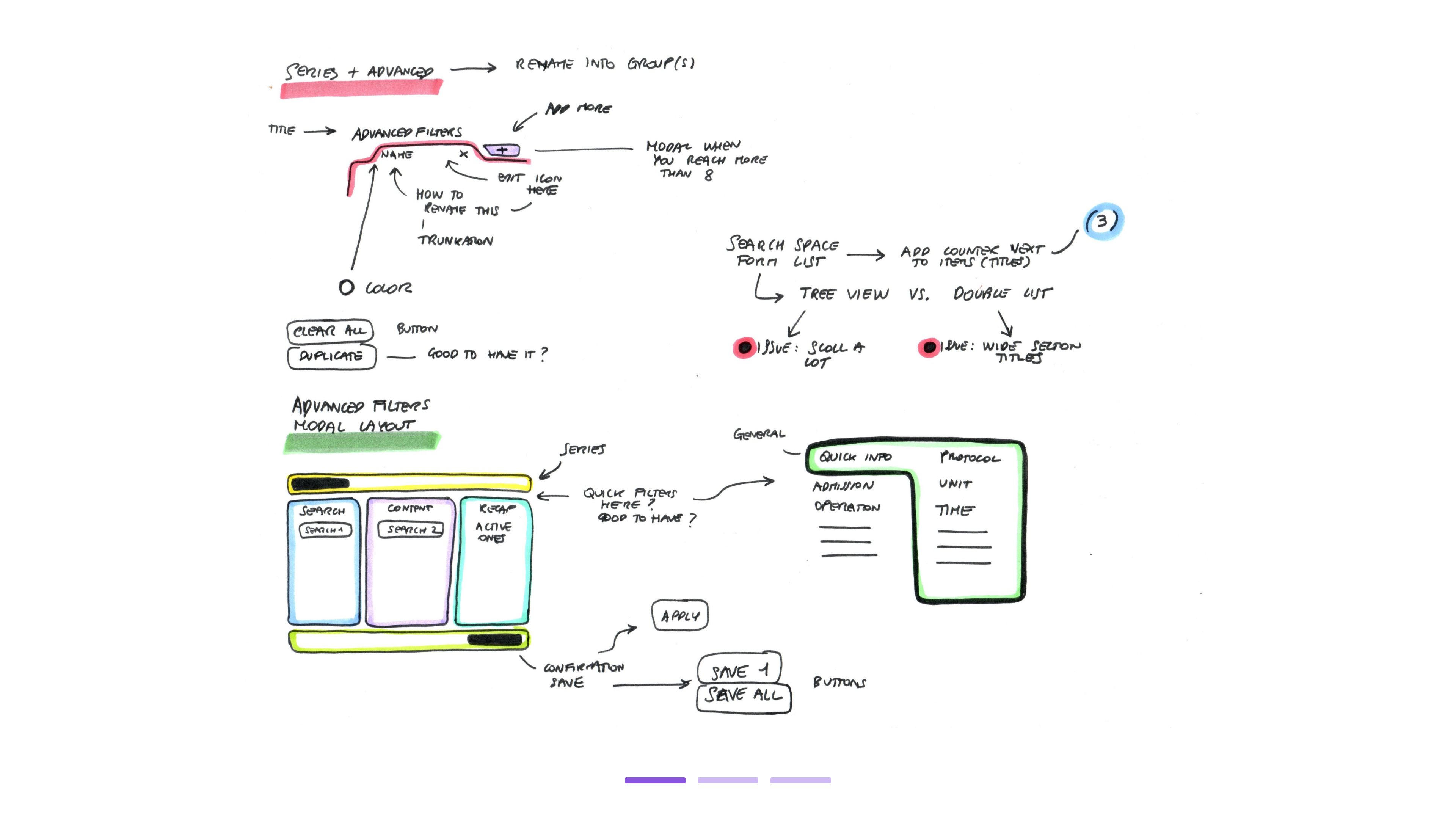
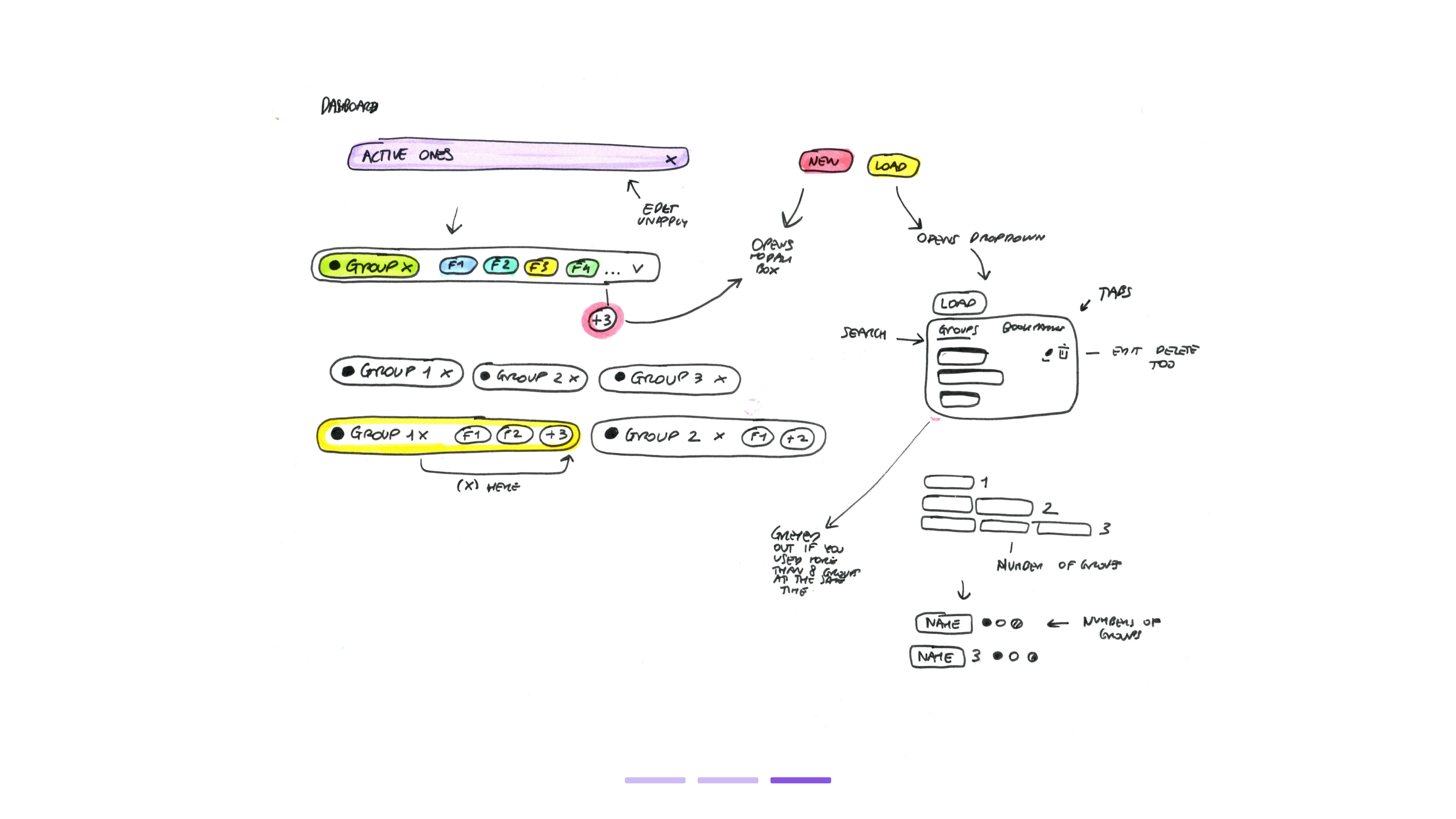
Development sketches

Samples of the previous filtering ecosystem